

By doing this all network traffic leaving your local network will exit encrypted and then sent through the Tor Network.
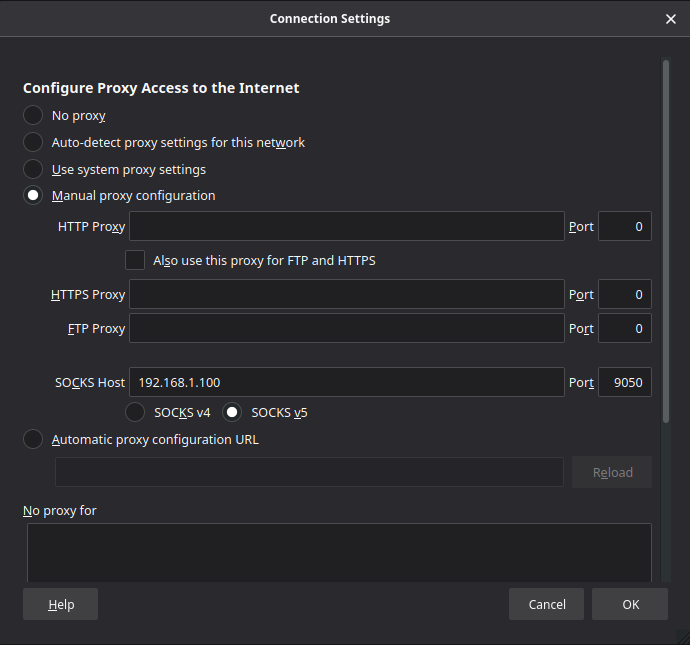
This guide will assist in configuring Tor as a transparent proxy and configure firewall rules to forward all network traffic regardless of TCP/UDP port through the Tor proxy. In many cases it is the interest of users to do more than tunnel just web browsing traffic. Transparent Proxies are proxies that do not need to be configured by an end-user in order to function. Traditionally proxy configurations must be set in every software package you with to use the proxy server (in most circumstances this is a web browser usually by means of specified port and/or username and password). Proxies are frequently used to mask the real location of a user, log traffic coming in and out of a network, circumvent network filtering, or in some cases to gain access to network resources that are local to the proxy but separated by a firewall or not directly available from a remote location.

A benefit of encryption is that it is not normally analyzed by network filters and therefor bypasses. Tor does not create complete anonymity but helps by encrypting and then bouncing your traffic around to other Tor relays before it exits an exit-node onto the Internet unencrypted. The Tor Project website can be used to gather more information about its use and how it works. Tor is a great product to help protect your anonymity online.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
